इस ब्लॉग को हिन्दी मे पढ़ने के लिए यहाँ क्लिक करे
Table of Contents
Introduction
Missed Abortion is a devastating experiences for expectant parents that often goes unnoticed until later stages. In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of “Missed Abortion” and shed light on its causes, symptoms, and management.
What is Missed Abortion?
Missed abortion, also known as a “silent miscarriage” or “delayed miscarriage,” refers to a situation where a fetus dies in the womb or uterus, but the body does not expel it immediately. The term “missed” implies that the loss of the pregnancy goes unnoticed for a prolonged period and is diagnosed on Sonography Report. Unlike other types of miscarriages, where the symptoms of pregnancy loss are evident, missed abortion can be particularly challenging because the body may not show any signs of a miscarriage.
Causes of Missed Abortion
Several factors can contribute to missed abortion. It’s essential to understand these causes to comprehend the risk factors and take appropriate precautions during pregnancy. Some of the common causes include:
1. Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chromosomal disorders in pregnancy can cause abortion in about 50% of cases. (Source: National Library of Medicine) During pregnancy, if an error occurs in the division of chromosomes, it can result in a chromosomal disorder. If understood in simple language, if there is some deficiency in the fetus at the time of fetus formation, then such a fetus does not develop naturally and abortion occurs. In some cases, if such a fetus develops and a child is born, then the child may show symptoms of chromosomal disorders such as Downs Syndrome. The mental and physical development of such children does not occur normally. Such children need special attention.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a vital role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. An imbalance in hormones, especially those responsible for supporting the pregnancy, can interfere with the fetus’s growth and development, leading to a missed abortion.
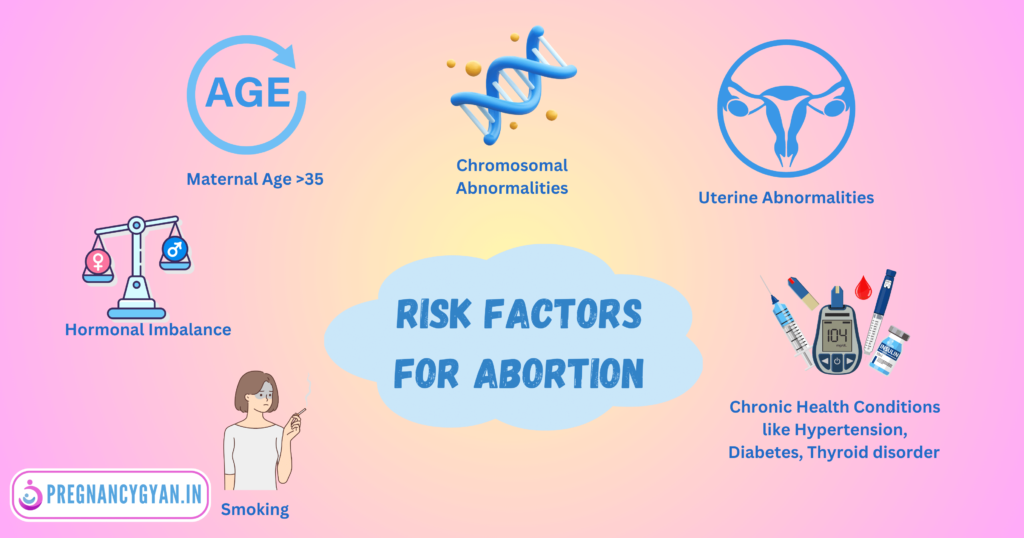
3. Maternal Age
The risk of miscarriage is related to the age of the mother. The older the pregnant mother, the greater is the risk of miscarriage, which also includes missed abortion. Because with the increasing age of women, the possibility of chromosomal abnormalities in the womb increases. Women over the age of 35 have a higher risk of miscarriage than younger women. The risk of abortion at the age of 35 is approximately 20 percent. At age 40, the risk is about 40 percent. And by the age of 45, it increases to about 80 percent.
4. Uterine Abnormalities
Anomalies in the shape or structure of the Uterus ( the organ in the lower body of a woman which carries a baby during pregnancy) can make it challenging for a fetus to grow and thrive, resulting in a missed abortion. Conditions like uterine fibroids or a septate uterus can interfere with successful implantation and pregnancy.
5. Chronic Health Conditions
Certain chronic health conditions, such as Diabetes, Hypertension and Thyroid disorders, Autoimmune or Endocrine disorders can increase the risk of miscarriage, including missed abortion. Proper management of these conditions before and during pregnancy is crucial to reduce the risk.
6. Smoking and Alcohol
If you smoke a lot or drink alcohol quite frequently, you may be more susceptible to missed abortion.
Missed Abortion Symptoms
Detecting missed abortion can be difficult, as there may be no apparent signs or symptoms. However, some women may experience subside of pregnancy symptoms. A decrease in pregnancy-related symptoms, such as morning sickness ( nausea, vomiting ) and breast tenderness, could indicate a problem.
Diagnosis

Diagnosing missed abortion typically involves a combination of methods, including:
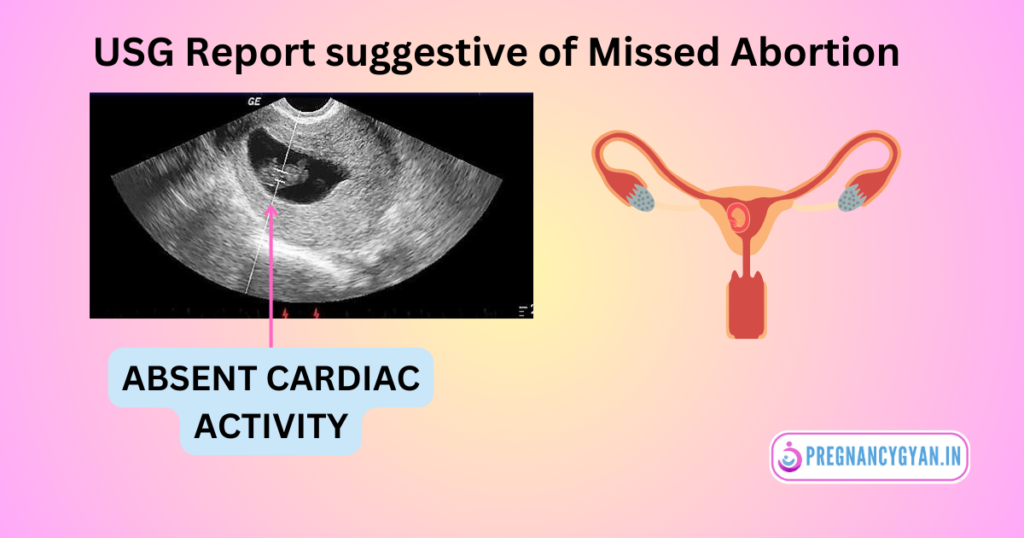
1. Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a crucial tool for diagnosing missed abortion. An ultrasound can confirm the absence of a fetal heartbeat and the cessation of fetal growth, indicating a missed abortion.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests to measure hormone levels, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), can help determine if the pregnancy is progressing as expected or if a missed abortion has occurred.
Missed Abortion Treatment
When faced with a missed abortion, expectant parents have several management options, depending on the gestational age and individual circumstances:
1. Expectant Management
In this method, we wait for the abortion to take place naturally and for the fetus to come out. The body eventually expels the fetus naturally. This process may take several weeks. If this is not successful, abortion may require medication or surgery.
2. Medical Management
Medical intervention involves using medications, such as Misoprostol, to induce the expulsion of the fetus and pregnancy tissues. This method may be preferred if expectant management takes too long or poses risks to the woman’s health. In most of the cases it usually takes about 6-8 hours for the abortion to occur after taking the tablets.
3. Surgical Management
Surgical procedures, such as dilation and evacuation (D&E), may be performed to remove the contents of the uterus. D and E is a type of day care surgery in which the damaged fetus is taken out of the uterus with a Suction Machine or MVA Syringe, thereby completing the abortion.
4. Emotional Support
Coping with a missed abortion can be emotionally distressing for both the woman and her partner. Seeking emotional support from family, friends, or support groups can be beneficial during this challenging time. It’s essential to acknowledge and express grief and seek professional counseling if needed.
Conclusion
Understanding missed abortion is essential for expectant parents and those planning to conceive. While it is a distressing experience, knowledge of its causes, symptoms, and management options can help individuals make informed decisions and seek timely medical attention. If anyone experiences symptoms of a missed abortion or has concerns about their pregnancy, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider promptly for appropriate evaluation and support.
FAQs
What is the main cause of missed abortion?
Chromosomal abnormalities is the most common case of missed abortion which can contribute in up to 50% cases.
What are the signs of a missed abortion?
In most of the cases missed abortion is diagnosed on a sonography report as there are no signs and symptoms of Missed Abortion. However, a decrease in pregnancy-related symptoms, such as morning sickness ( nausea, vomiting ) and breast tenderness, could indicate a problem.
How long can a missed abortion last?
If undiagnosed, Missed Abortion can last three to four weeks. It is usually diagnosed on USG repot.
What is the difference between a Missed abortion and a complete abortion?
In missed abortion fetus heart beats stop without showing any symptom and it is diagnosed after a Sonography report. In complete abortion there are symptoms like pain in lower abdomen and per vaginal bleeding which expel the fetus completely out of the body after which bleeding stops. Missed abortion needs treatment to expel the fetus out of the body while after complete abortion confirmed by the usg report no treatment needed to expel the fetus.
How can I prevent a missed abortion?
Missed abortion cannot always be prevented, but the risks can be reduced by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding harmful substances like alcohol and smoking, treatment of uncontrolled Diabetes and Hypertension before getting pregnant, and seeking prenatal care on time.
Is it easy to conceive after missed abortion?
After a miscarriage, you can become pregnant as soon as two weeks later. Consult your healthcare professional for advice once you feel both physically and emotionally prepared to become pregnant after a miscarriage. There might not be a need to wait to get pregnant after a single miscarriage.

1 thought on “Missed Abortion : Causes, Symptoms, and Management”