इस ब्लॉग को हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए यहाँ क्लीक करे।
Pregnancy is a journey filled with excitement and anticipation. One of the magical moments for many expectant parents is the first glimpse of their growing baby. Thanks to modern technology, ultrasound scans make it possible to see inside the womb and witness the early stages of life. In this blog know about the world of Ultrasound in Pregnancy, understanding its significance, uses, and potential benefits and limitations.
Table of Contents
What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound, often referred to as Sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside parts of the body. Ultrasound machines send out sound waves into the body. These waves bounce back when they hit different parts inside the body . The Sonography machine then uses these bounced-back waves to make an image showing different parts of the body. In Pregnancy, it allows healthcare providers to visualize and monitor the growth of the baby growing inside the mothers womb. Note that Ultrasound waves are not harmful to baby hence Ultrasound is completely safe during Pregnancy.
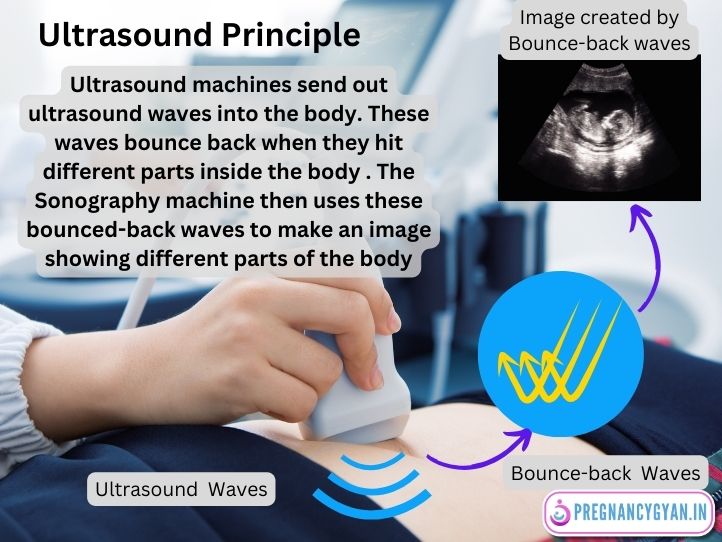
Why is Ultrasound Done in Pregnancy ?
Ultrasounds in pregnancy are performed to monitor fetal development, ensure the baby’s well-being, and detect any potential abnormalities or complications early on. They offer valuable insights into the baby’s growth and the health of the pregnancy.
When is Ultrasound Done in Pregnancy ?
During Pregnancy usually 5 Ultrasounds done at different gestational ages of Pregnancy for different reasons. Gestational age is calculated in weeks from the first day of the last menstrual period. These Ultrasounds in Pregnancy are as follows:
- Dating Scan : at 7 to 8 weeks of Pregnancy.
- NT Scan : at 11 to 13 weeks of Pregnancy.
- Anomaly Scan or Level II Scan : at 18 to 22 weeks of Pregnancy.
- Growth Scan 1: at 28 to 32 weeks of Pregnancy.
- Growth Scan 2: at 32 to 38 weeks of Pregnancy:

Note that your Doctor may ask you to do more than 5 ultrasound scans if there is any concern about the development of the baby.
Let’s see each Scan in detail.
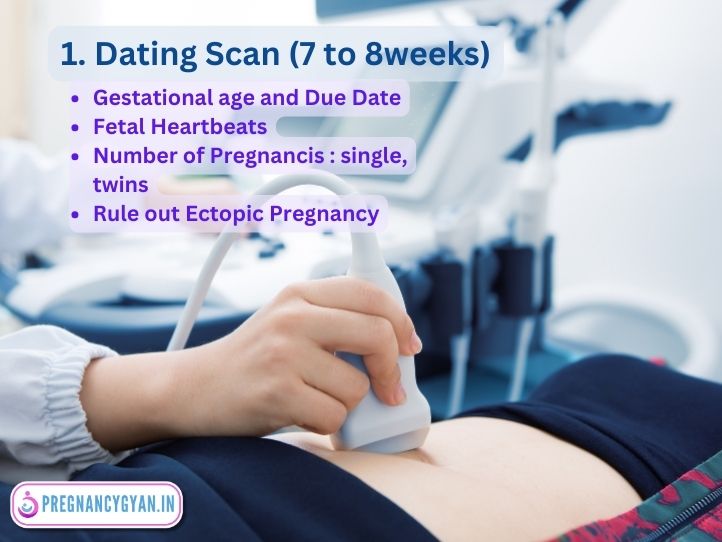
1. Dating Scan
A Dating scan, typically performed in 7 to 8 weeks of Pregnancy.
Importance:
- To accurately determine the gestational age of the fetus. It is very helpful in Pregnant mothers who do not remember the date of the last menstrual period or have irregular periods before pregnancy.
- Establishing Due Date or expected date of delivery ( EDD ) ensuring appropriate prenatal care and monitoring.
- Cardiac Activity : Fetal Heartbeats can be noted at 7 weeks of pregnancy.
- Rule out ectopic pregnancy : It can detect whether a fetus is inside or outside the uterine cavity.
- Identifying Multiple Pregnancies: This scan can detect if there’s more than one fetus, which might require specialized care.
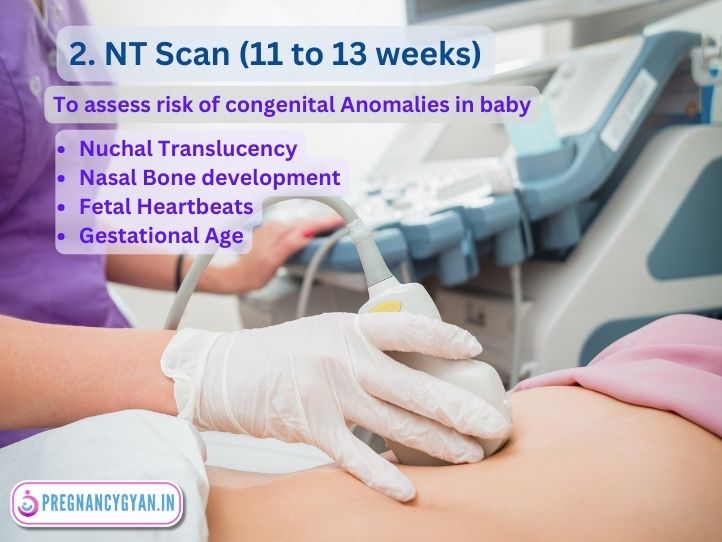
2. NT (Nuchal Translucency) Scan
It Is Conducted between 11 to 13 weeks of Pregnancy. NT scan measures the clear space in the tissue at the back of the baby’s neck.
Importance:
- Screening for Down Syndrome: An increased nuchal translucency measurement might indicate a higher risk for chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome.
- Early Detection: It offers an early opportunity to assess potential risks, allowing parents to make informed decisions about further diagnostic tests and if needed termination of pregnancy.
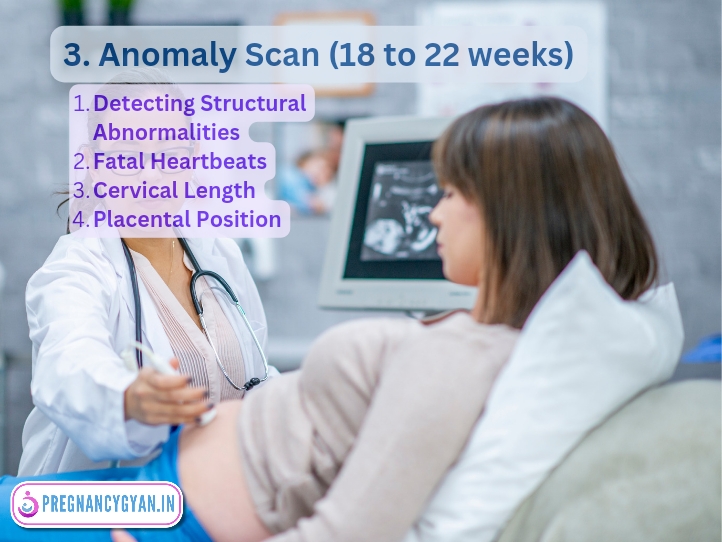
3. Level 2 ultrasound in pregnancy
or Anomaly Scan
It Is typically performed between 18 and 22 weeks, the anomaly scan provides a detailed examination of the fetus’s anatomy or strucure of body parts.
Importance:
- Detecting Structural Abnormalities: This scan assesses the fetus’s organs, limbs, spine, and more, identifying any structural abnormalities.
- Reassurance: A normal anomaly scan can provide significant reassurance to parents regarding their baby’s health and development.
- Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis of Structural Abnormalities in a baby can help the couple to make informed design about termination of Pregnancy.
4. Growth Scan 1
This scan is conducted in 28 to 32 weeks of Pregnancy. It monitors the fetus’s growth by measuring specific parameters like the head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length.
Importance:
- Assessing Fetal Growth: It helps determine if the fetus is growing at an expected rate, ensuring there are no growth restrictions or excessive fetal growth.
- Identifying Potential Concerns: Discrepancies in growth parameters might indicate underlying issues, prompting further evaluations or interventions.
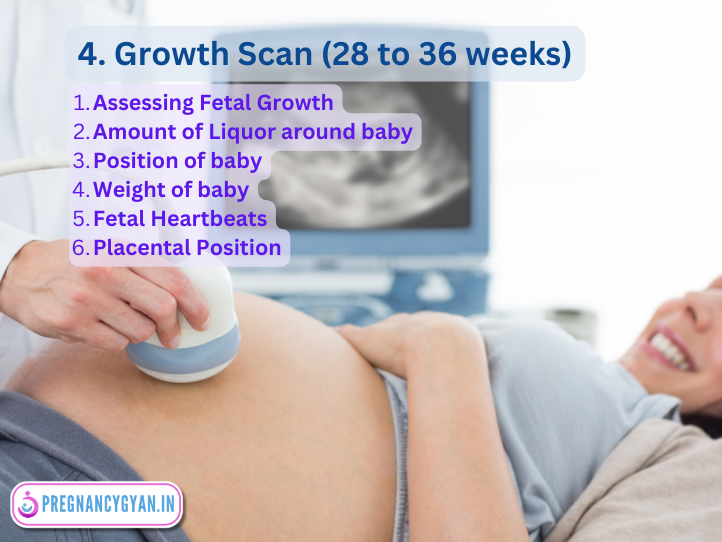
5. Growth Scan 2
This scan is conducted in 32 to 36 weeks of Pregnancy. This growth scan may be conducted to continue monitoring the fetus’s development in the late third trimester.
Importance:
- Monitoring Late-Term Growth: This scan ensures that the fetus continues to grow appropriately, especially in the crucial final weeks before birth.
- Planning for Birth: Accurate information about the baby’s size and growth helps healthcare providers plan for a safe delivery, especially if there are concerns about fetal size or position.
Types of Ultrasounds
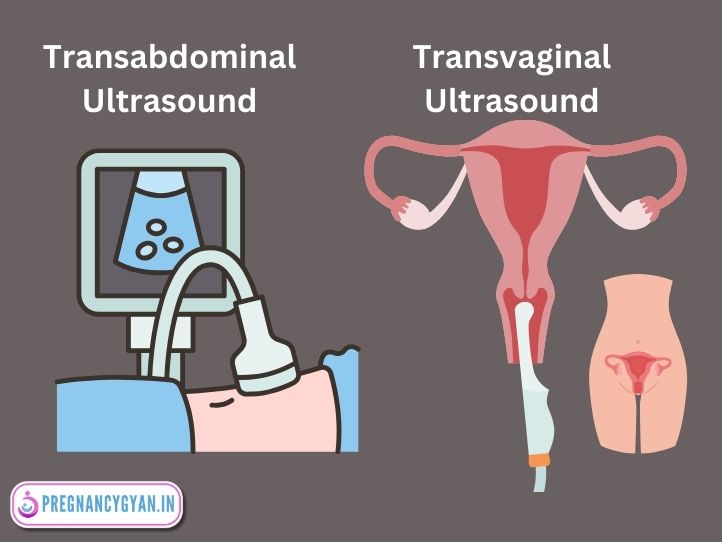
1. Transabdominal Ultrasound:
The Sonography probe is moved over the abdomen, emitting sound waves that bounce back, creating an image. This is the most common type of ultrasound in pregnancy.
2. Transvaginal Ultrasound ( TVS )
In early Pregnancy or when clearer images are needed, a sonography probe is inserted into the vagina, closer to the uterus. The vagina is a muscular tube in females that connects the uterus to the external genitals and serves as a passage for menstrual flow, intercourse, and childbirth.
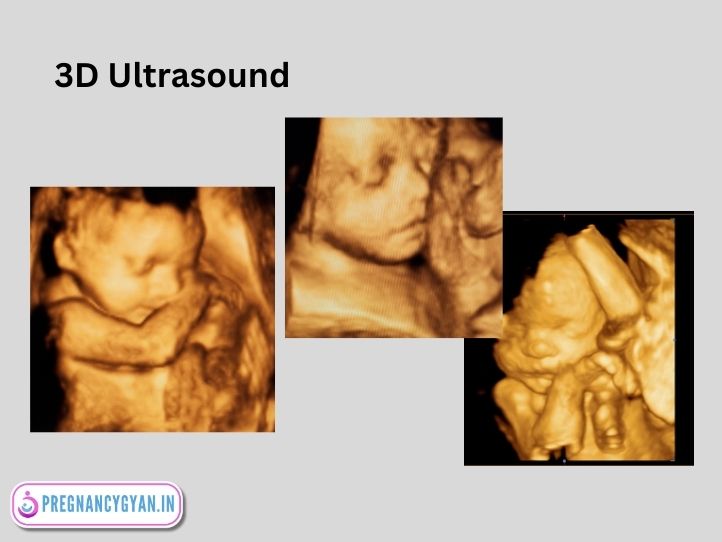
3. 3D and 4D Ultrasounds
These advanced techniques provide three-dimensional images, allowing a more detailed view of the fetus. 4D adds the element of motion, capturing real-time movements.
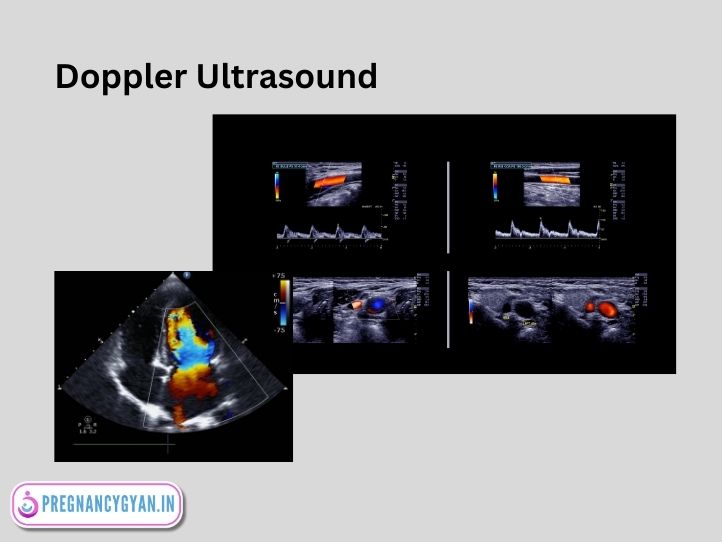
4. Doppler Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Doppler ultrasound in pregnancy measures blood flow to the growing baby helping healthcare professionals assess fetal well-being by monitoring the placental and fetal circulation. It aids in detecting potential complications and ensuring proper oxygen and nutrient supply to the developing fetus. It is very helpful in High Risk Pregnancy like Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH), Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR).
Benefits
– Early Detection: Ultrasounds can identify multiple pregnancies, potential complications, or issues early on, allowing for timely interventions.
– Medical Decision Making: In cases of potential complications, ultrasounds guide medical decisions, ensuring the best outcomes for mother and child.
– Bonding: For parents, seeing their baby’s image can strengthen the emotional bond, making the Pregnancy feel more real.
Limitations
Ultrasound in pregnancy may have limitations in accurately determining certain fetal abnormalities, and its effectiveness can be hindered by factors such as maternal obesity or fetal positioning, leading to potential diagnostic challenges. Additionally, ultrasound imaging may not always provide detailed information on certain structural anomalies or genetic conditions.
Conclusion
Ultrasound in Pregnancy has transformed prenatal care, offering a window into the womb and reassuring parents about their baby’s well-being. Ultrasound technology has significantly enhanced prenatal care, enabling healthcare professionals to closely monitor fetal development and ensure the well-being of both mother and child.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many times do you get an ultrasound during pregnancy?
Minimum 4 Ultrasound Scans advised during normal Pregnancy at different gestational ages of pregnancy as follows. Gestational age is calculated as the number of weeks from the first day of the last menstrual period.
- Dating Scan : at 7 to 8 weeks of Pregnancy.
- NT Scan : at 11 to 13 weeks of Pregnancy.
- Anomaly Scan or Level II Scan : at 18 to 22 weeks of Pregnancy.
- Growth Scan : at 28 to 38 weeks of Pregnancy.
When is doppler ultrasound done in pregnancy?
Doppler ultrasound in pregnancy is typically performed after 20 weeks, during the second trimester and beyond. It assesses blood supply to the baby in the umbilical cord and other fetal vessels, aiding in monitoring the well-being of the developing fetus. It is very helpful in High Risk Pregnancy like Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH), Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR).
What is level 2 ultrasound in pregnancy?
A level 2 ultrasound in pregnancy, also known as an Anomaly Scan or Anatomical ultrasound, is a comprehensive scan typically performed in the second trimester between 18 to 22 weeks of Pregnancy. It assesses fetal anatomy, identifying any structural abnormalities and providing a more in-depth examination than a routine screening ultrasound.
In which week of pregnancy first ultrasound is done?
The first ultrasound in pregnancy is typically done around the 7 to 8 weeks, known as the Dating Scan or Viability Scan, to confirm the pregnancy, note fetal heartbeats, estimate the due date, and check for multiple pregnancies or any early complications.
How soon can an ultrasound detect pregnancy?
An ultrasound can detect pregnancy as early as 4 to 6 weeks after the last menstrual period, visualizing the gestational sac and confirming the presence of an embryo.
When can a fetal heartbeat be detected by ultrasound?
A fetal heartbeat can be detected by ultrasound after 6 weeks of pregnancy.
Can repeated Ultrasound in Pregnancy cause harm to the baby?
No, repeated ultrasounds in pregnancy are generally considered safe and have not been shown to cause harm to the baby.

1 thought on “Ultrasound in Pregnancy”